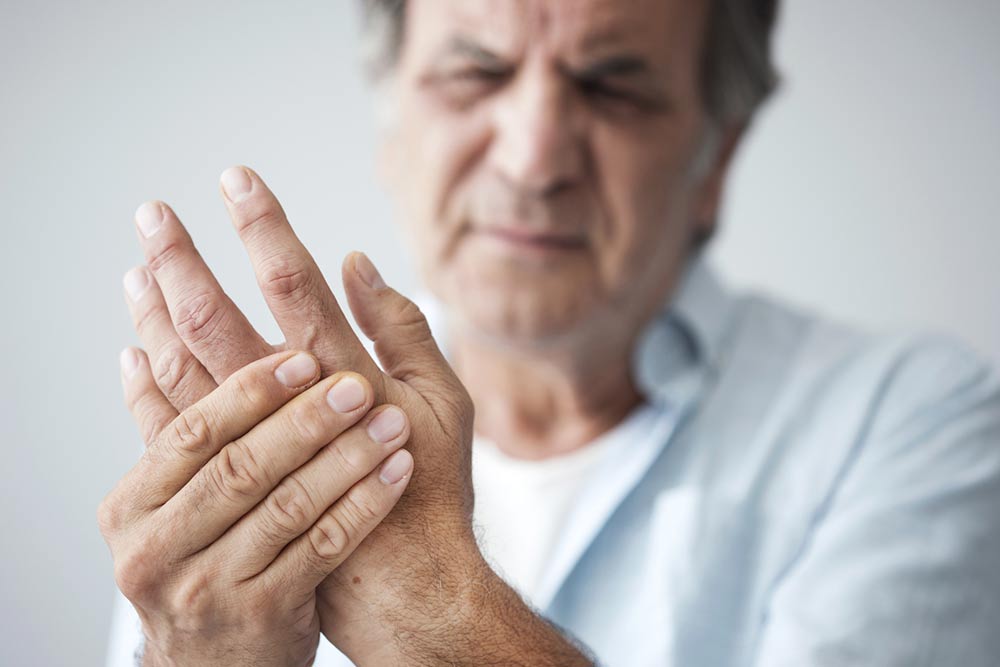
Rheumatoid Arthritis – Risk Factors and Management Options
Rheumatoid arthritis is an inflammatory disease that develops when the immune system attacks the healthy tissue lining the joints. This condition mainly affects the joints in the hands, wrists, and knees but can also affect other parts of the body, including organs like the lungs and heart. The condition typically causes pain, swelling, and stiffness in the joints, which can be managed with timely treatment. Here are a few other things to know:
Risk factors
Certain risk factors can increase the risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis:
1. Age and gender
Though rheumatoid arthritis can develop at any age, the risk is higher in those over 60. Further, women are more likely than men to get rheumatoid arthritis. Female hormones are believed to contribute to an increased risk of the condition.
2. Family history
The risk of developing this inflammatory condition is higher in those with a close family member diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis.
3. Environmental factors and lifestyle habits
Exposure to toxins, pollutants, and chemicals in the environment may also increase the risk of rheumatoid arthritis. Further, those who smoke or are exposed to smoke regularly are also at an increased risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis. Additionally, p rolonged stress can be a risk factor.
Management options
The treatment for rheumatoid arthritis mainly focuses on reducing inflammation, improving joint function, and managing overall well-being. Some of the options for treating rheumatoid arthritis include:
1. Prescription treatment
Medication is often prescribed to manage the condition. For instance, anti-inflammatory options and corticosteroids can help reduce pain and inflammation associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Disease-modifying antirheumatic options help slow the progression of rheumatoid arthritis by modifying the immune system.
2. Surgery
Surgery may be required to repair severely damaged joints. Joint replacement or arthroplasty is an option for replacing part or all of a joint.
3. Complementary therapies
Certain therapies work alongside medications for managing symptoms and improving movement. For instance, acupuncture is a procedure in which small needles are inserted into the skin to relieve pain and inflammation in the joints. Further, those with rheumatoid arthritis can also benefit from massage, as it is known to improve blood circulation and reduce pain and stiffness in the joints.
4. Home remedies
Those with rheumatoid arthritis may also benefit from using heat pads, taking warm showers, or applying cold compresses. This can help reduce stiffness and pain in the affected joints when dealing with rheumatoid arthritis. Further, getting adequate rest can help reduce pain and inflammation. Managing stress is also a key part of management. So, one can try relaxation techniques like deep breathing exercises and meditation to keep stress in check.
5. Exercise
Getting in some movement during the day can help in maintaining the motion in the joints and increasing mobility when dealing with rheumatoid arthritis. Here, low-impact exercises such as walking or swimming may help restore joint motion and increase strength.
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic condition which can often flare up. Although there is no cure, early diagnosis and treatment can help in managing the symptoms, reducing joint damage, and preventing further complications.